
NAVYPEDIA
 Support the project with paypal
Support the project with paypal
Photo

Gymnôte 1970 Many thanks to Wolfgang Stöhr for additional information on this page.
Ships
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gymnôte | S655 | Q73 | Arsenal de Cherbourg | 17.3.1963 | 17.3.1964 | 17.10.1966 | stricken 4.1987 |
Technical data
| Displacement standard, t | |
|---|---|
| Displacement normal, t | 3000 / 3250 |
| Length, m | 84.0 |
| Breadth, m | 10.6 |
| Draught, m | 7.60 |
| No of shafts | 2 |
| Machinery | 4 SEMT-Pielstick diesel-generators, 2 electric motors |
| Power, h. p. | 2600 / 2600 |
| Max speed, kts | 11 / 10 |
| Fuel, t | diesel oil |
| Endurance, nm(kts) | 5500(7) / |
| Armament | 4 M-1 SLBM (4 M-1) |
| Electronic equipment | Calypso II radar, DUUA-1 sonar |
| Complement | 78 |
| Diving depth operational, m | 150 |
Standard scale images
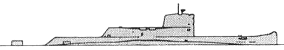
Gymnôte 1966
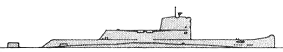
Gymnôte 1980
Graphics
Project history
In 1954 studies were made of a torpedo-armed nuclear-powered submarine; the boat was even laid down at Cherbourg in 1956 as hull No Q244. A surface displacement of 4000t on a length of 120m was projected. The inability of the French to produce enriched uranium at this time meant, however, that a heavy-water reactor using unrefined uranium was the only possible propulsion plant. This proved too heavy and construction was halted in 1958. Negotiations with the Americans for the purchase of a reactor failed, and even the purchase of enriched uranium was refused except for land experimental use. The project was abandoned in 1959.
With the decision to develop an independent sea-based deterrent force, it was decided to complete the hull (now designated Q251) as an experiment submarine for the testing of the new ballistic missiles. A prominent casing abaft the fin housed four vertical launch tubes. Gymnôte was also fitted with the prototype guidance and inertial navigation system intended for Le Redoutable.
Modernizations
1979: - 4 M-1 SLBM; + 2 M-4 SLBM (2 M-4)
Naval service
No significant events.
Many thanks to Wolfgang Stöhr for additional information on this page.
 HOME
HOME FIGHTING SHIPS OF THE WORLD
FIGHTING SHIPS OF THE WORLD FRANCE
FRANCE SUBMARINES
SUBMARINES GYMNÔTE ballistic missile trials submarine (1966)
GYMNÔTE ballistic missile trials submarine (1966)
