
NAVYPEDIA
 Support the project with paypal
Support the project with paypal
Photo

Sydney 1974
Ships
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sydney (ex-Terrible) | R17, 1969- 17 | Devonport DYd, UK | 19.4.1943 | 30.9.1944 | 5.2.1949 | stricken 7.1973, sold 10.1975 | |
| Melbourne (ex-Majestic) | R21, 1969- 21 | Vickers-Armstrong, Barrow, UK | 15.4.1943 | 28.2.1945 | 8.11.1955 | stricken 11.1983, BU 1985 |
Technical data
| Data variant | R17 | R21 |
|---|---|---|
| Displacement standard, t | 14000 |
16000 |
| Displacement full, t | 17780 |
19966 |
| Length, m | 192.0 pp 211.8 oa |
198.1 pp 213.8 oa |
| Breadth, m | 24.4 |
24.5 hull, 38.4 fd |
| Draught, m | 7.01 deep load |
7.80 |
| No of shafts | 2 |
2 |
| Machinery | 2 sets Parsons geared steam turbines, 4 Admiralty 3-drum boilers |
2 sets Parsons geared steam turbines, 4 Admiralty 3-drum boilers |
| Power, h. p. | 40000 |
42000 |
| Max speed, kts | 25 |
24 |
| Fuel, t | oil 3480 |
oil 3200 |
| Endurance, nm(kts) | 12000(14) | 12000(14) |
| Armament | 6 x 2 - 40/60 RP.50 Mk V, 18 x 1 - 40/60 Mk VII, 26 aircraft (Sea Fury, Firefly fighters) |
7 x 2 - 40/60 Mk 5, 11 x 1 - 40/60 Mk 7, 24 aircraft (Sea Fury, Firefly fighters, Firefly, Gannet ASW planes, Sea Otter rescue amphibians) |
| Electronic equipment | 2x type 277Q, type 293M, type 960/281BQ, type 961 radars |
3x type 277Q, type 293Q, type 978 radars |
| Complement | 1300 | 1417 as flagship |
Air group
| Year | Fighters | Attackers | other planes | Helicopters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950, Sydney | 12 Sea Fury FB.11, | --- | 22 Firefly AS.4, 2 Sea Otter | --- |
| 1951, Sydney | 22 Sea Fury FB.11 | --- | 12 Firefly AS.4 | --- |
| 1956, Melbourne | 8 Sea Venom FAW.53 | --- | 17 Gannet AS.1 | 2 Sycamore HR.50 |
| 1963, Melbourne | 10 Sea Venom FAW.53 | --- | 10 Gannet AS.1 | 8 Wessex HAS.31 |
| 1975, Melbourne | --- | 8 A-4G Skyhawk | 6 S-2E Tracker | 10 Wessex HAS.31B |
| 1980, Melbourne | --- | 8 A-4G Skyhawk | 4 S-2G Tracker | 5 Sea King HAS.50 |
Standard scale images
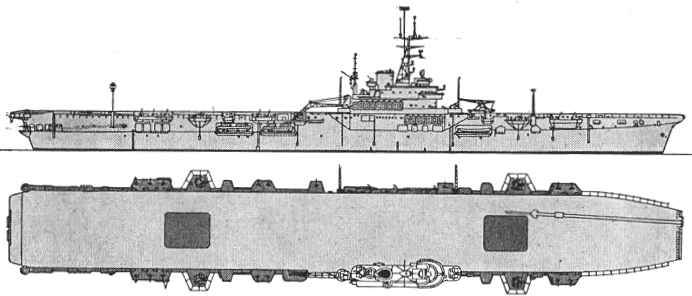
Sydney 1963
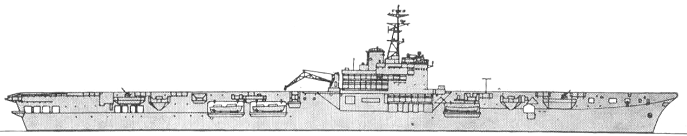
Sydney 1968
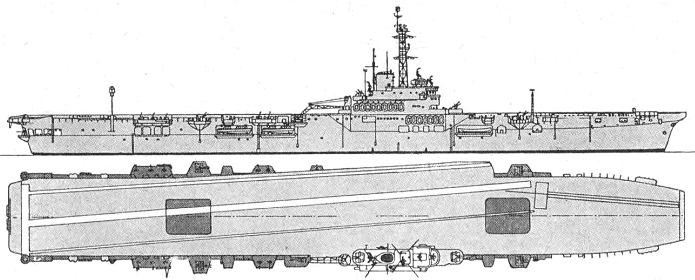
Melbourne 1968
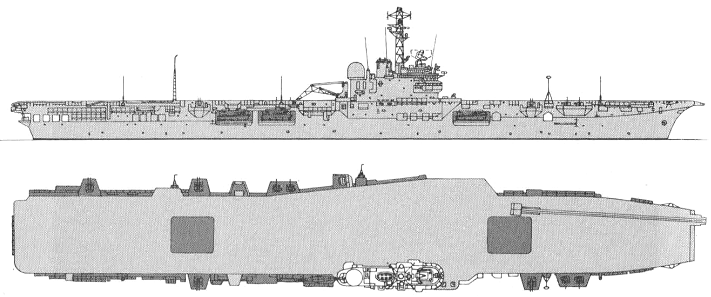
Melbourne 1978
Graphics
Aircraft facilities
Sydney: (fd - 5,131m², ha - 2,142m² / 11,355m³), Flight deck: 210.3x24.4m; hangar: 135.6x15.8x 5.3m. Two lifts: 16.5x10.4m, 6.8t. 1 catapult BH-III (6.4t plane was launched at 122 km/h). Aircraft fuel stowage: 303,000l.
Melbourne:(fd ~ 6,500m², ha - 2,142m² / 11,355m³), Flight deck: 213.8x38.4m; hangar: 135.3x15.8x 5.3m. Two lifts: 17.7x12.2m, 11t. 1 catapult BS-4. Aircraft fuel stowage: 802,000l of jet fuel and 18,900l of petrol.
Project history
Majestic class HMS Terrible became HMAS Sydney.
Work was resumed on HMS Majestic in 1949 after her purchase by the Australian government, and the opportunity was taken to incorporate as many new ideas as possible, including a steam catapult, a 6° angled deck and mirror landing sights. However, apart from a lattice mast and whip aerials she looked similar to the original Majestics.
A greatly enhanced radar suite was incorporated, including three Type 277Q height-finding sets.
Protection
There were mantlets around aircraft torpedoes warheads rooms only. Their thickness was 10mm. Longitudinal watertight bulkheads covered the machinery.
Modernizations
1963, Sydney: became fast military transport: - 6 x 2 - 40/60, 14 x 1 - 40/60; vehicles were carried on deck, hangar was used for troop accommodation
11/1968, Melbourne: - 3 x 2 - 40/60, 7 x 1 - 40/60; + LW-02, ZW, SPN-35 radars, ECM equipment
1969, Sydney: + 6 LCPU (on davits)
1971, Melbourne: catapult was rebuilt, deck was strengthened.
Naval service
HMAS Sydney saw considerable active service in the Korean War alongside her British sisters. Melbourne was laid up to reserve in 1976. Melbourne sunk two destroyers by collisions (HMAS Voyager 10.2.1964 in Tasman Sea and USS Frank E. Evans 3.6.1969 in South China Sea), receiving nickname 'destroyer killer'.
 HOME
HOME FIGHTING SHIPS OF THE WORLD
FIGHTING SHIPS OF THE WORLD AUSTRALIA
AUSTRALIA AIRCRAFT CARRYING SHIPS
AIRCRAFT CARRYING SHIPS SYDNEY light aircraft carriers (1949-1955)
SYDNEY light aircraft carriers (1949-1955)

